Python: Arbitrary Waveform Generator
-
Moku:Go
Moku:Go Arbitrary Waveform Generator Moku:Go Data Logger Moku:Go Frequency Response Analyzer Moku:Go Logic Analyzer & Pattern Generator Moku:Go Oscilloscope & Voltmeter Moku:Go PID Controller Moku:Go Spectrum Analyzer Moku:Go Waveform Generator Moku:Go Power Supplies Moku:Go Digital Filter Box Moku:Go FIR Filter Builder Moku:Go Lock-in Amplifier Moku:Go General Moku:Go Logic Analyzer/Pattern Generator Moku:Go Time & Frequency Analyzer Moku:Go Laser Lock Box Moku:Go Phasemeter
-
Moku:Lab
Moku:Lab General Moku:Lab Arbitrary Waveform Generator Moku:Lab Data Logger Moku:Lab Digital Filter Box Moku:Lab FIR Filter Builder Moku:Lab Frequency Response Analyzer Moku:Lab Laser Lock Box Moku:Lab Lock-in Amplifier Moku:Lab Oscilloscope Moku:Lab Phasemeter Moku:Lab PID Controller Moku:Lab Spectrum Analyzer Moku:Lab Waveform Generator Moku:Lab Time & Frequency Analyzer Moku:Lab Logic Analyzer/Pattern Generator
-
Moku:Pro
Moku:Pro Arbitrary Waveform Generator Moku:Pro Data Logger Moku:Pro Frequency Response Analyzer Moku:Pro Oscilloscope Moku:Pro PID Controller Moku:Pro Spectrum Analyzer Moku:Pro Waveform Generator Moku:Pro Lock-in Amplifier Moku:Pro Digital Filter Box Moku:Pro FIR Filter Builder Moku:Pro Phasemeter Moku:Pro Multi-instrument Mode Moku:Pro General Moku:Pro Logic Analyzer/Pattern Generator Moku:Pro Time & Frequency Analyzer
- Python API
- MATLAB API
- Arbitrary Waveform Generator
- Data Logger
- Digital Filter Box
- FIR Filter Builder
- Frequency Response Analyzer
- Laser Lock Box
- Lock-in Amplifier
- Oscilloscope
- Phasemeter
- PID Controller
- Spectrum Analyzer
- Time & Frequency Analyzer
- Waveform Generator
- Logic Analyzer & Pattern Generator
- Multi Instrument Mode
- Moku Cloud Compile
- Moku general
- LabVIEW
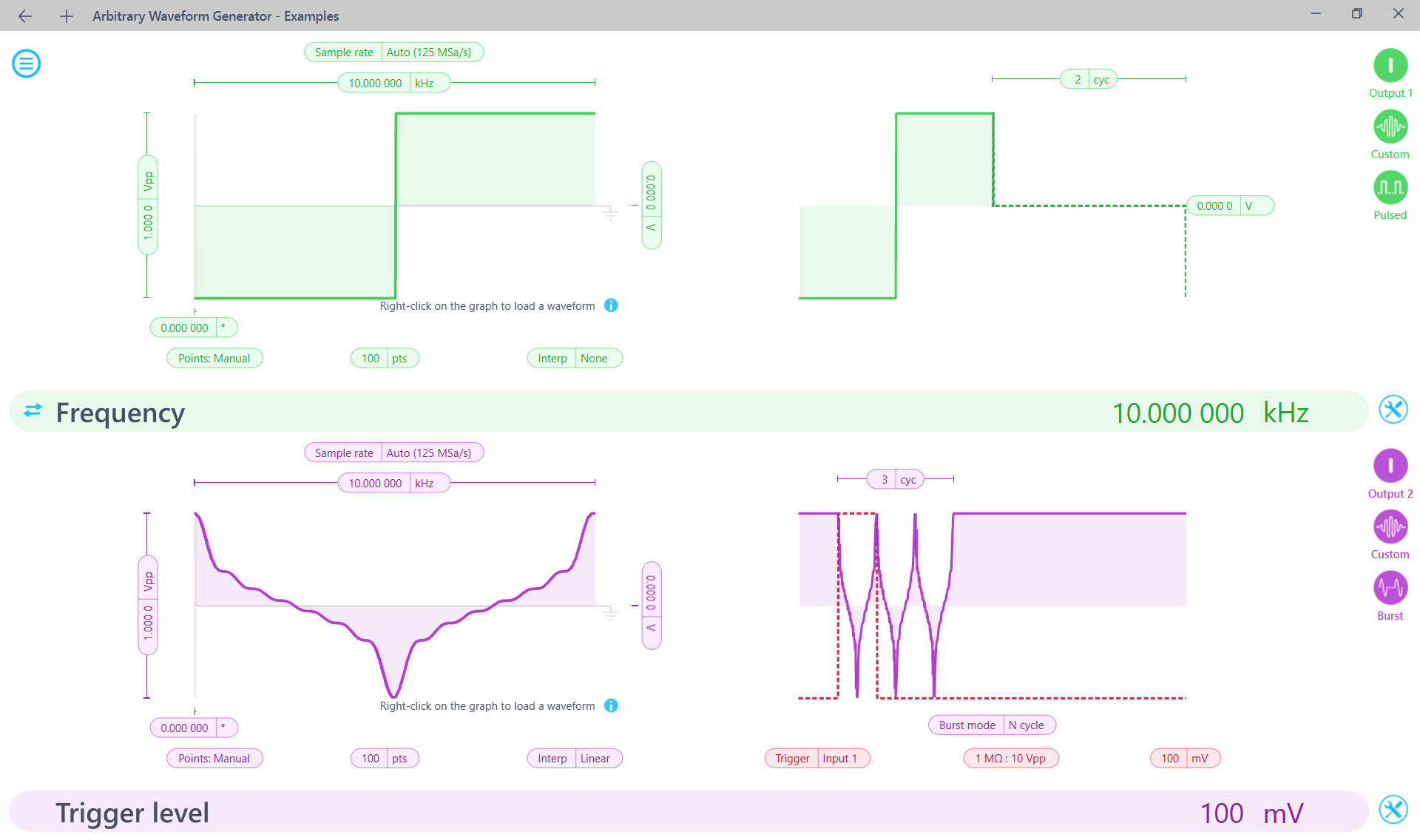
Example Python script to implement the Arbitrary Waveform Generator
To observe the burst-modulated behavior of the signal on Channel 2, it is recommended to connect a 2 kHz Square wave to Input 1 of your Moku
#
# moku example: Arbitrary Waveform Generator
#
# This example demonstrates how you can generate and output arbitrary
# waveforms using the Moku Arbitrary Waveform Generator
#
# (c) 2024 Liquid Instruments Pty. Ltd.
#
import numpy as np
from moku.instruments import ArbitraryWaveformGenerator
# Generate two signals for the Arbitrary Waveform Generator to output
t = np.linspace(0, 1, 100) # Evaluate our waveform at 100 points
# Simple square wave (can also use scipy.signal)
sq_wave = np.array([-1.0 if x < 0.5 else 1.0 for x in t])
# More interesting waveform. Note that we have to normalize this waveform
# to the range [-1, 1]
not_sq = np.zeros(len(t))
for h in np.arange(1, 15, 2):
not_sq += (4 / (np.pi * h)) * np.cos(2 * np.pi * h * t)
not_sq = not_sq / max(abs(not_sq))
# Connect to your Moku by its ip address ArbitraryWaveformGenerator('192.168.###.###')
# or by its serial ArbitraryWaveformGenerator(serial=123)
i = ArbitraryWaveformGenerator('192.168.###.###', force_connect=False)
try:
# Load and configure the waveform.
i.generate_waveform(channel=1, sample_rate='Auto',
lut_data=list(sq_wave), frequency=10e3,
amplitude=1, interpolation=False)
i.generate_waveform(channel=2, sample_rate='Auto', lut_data=list(not_sq),
frequency=10e3, amplitude=1, interpolation=True)
# Set Channel 1 to Pulse mode
# 2 dead cycles at 0Vpp
i.pulse_modulate(channel=1, dead_cycles=2, dead_voltage=0)
# Set Channel 2 to Burst mode
# Burst mode triggering from Input 1 at 0.1 V
# 3 cycles of the waveform will be generated every time it is triggered
i.burst_modulate(channel=2, trigger_source='Input1', trigger_mode='NCycle',
burst_cycles=3, trigger_level=0.1)
except Exception as e:
print(f'Exception occurred: {e}')
finally:
# Close the connection to the Moku device
# This ensures network resources and released correctly
i.relinquish_ownership()