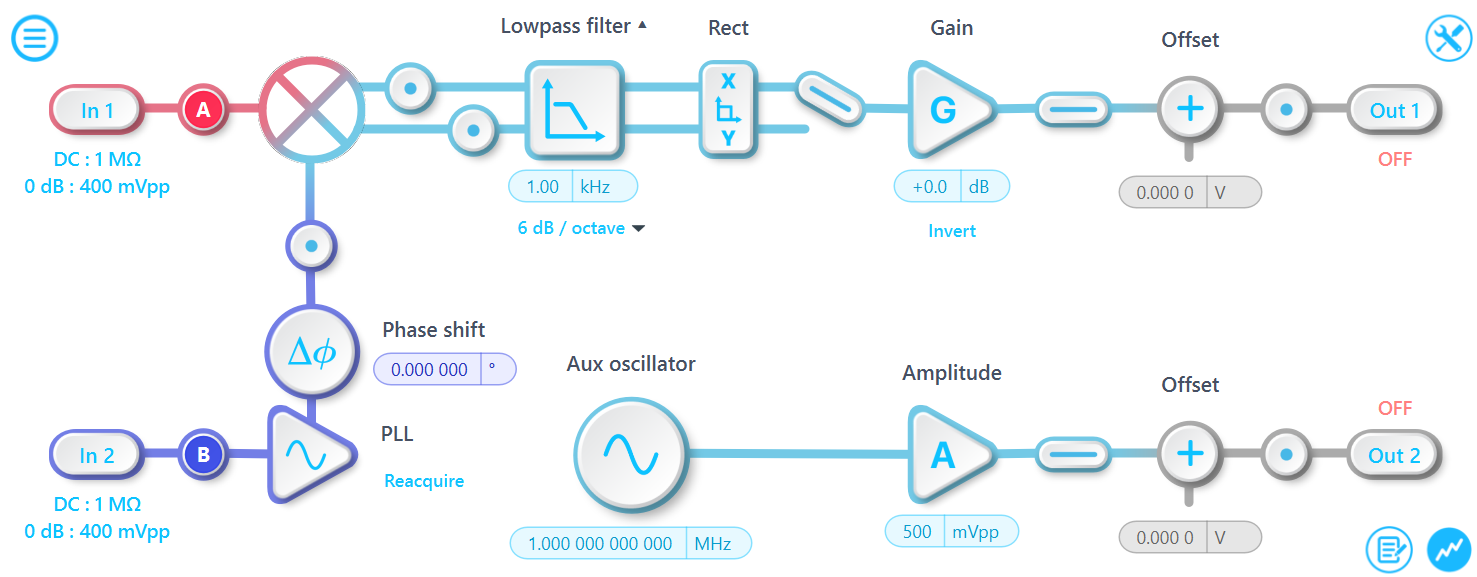
What's the difference between external and external (PLL) mode?
-
Moku:Go
Moku:Go General Moku:Go Arbitrary Waveform Generator Moku:Go Data Logger Moku:Go Digital Filter Box Moku:Go FIR Filter Builder Moku:Go Frequency Response Analyzer Moku:Go Logic Analyzer & Pattern Generator Moku:Go Oscilloscope & Voltmeter Moku:Go PID Controller Moku:Go Spectrum Analyzer Moku:Go Waveform Generator Moku:Go Power Supplies Moku:Go Lock-in Amplifier Moku:Go Time & Frequency Analyzer Moku:Go Laser Lock Box Moku:Go Phasemeter
-
Moku:Lab
Moku:Lab General Moku:Lab Arbitrary Waveform Generator Moku:Lab Data Logger Moku:Lab Digital Filter Box Moku:Lab FIR Filter Builder Moku:Lab Frequency Response Analyzer Moku:Lab Laser Lock Box Moku:Lab Lock-in Amplifier Moku:Lab Oscilloscope Moku:Lab Phasemeter Moku:Lab PID Controller Moku:Lab Spectrum Analyzer Moku:Lab Time & Frequency Analyzer Moku:Lab Waveform Generator Moku:Lab Logic Analyzer/Pattern Generator
-
Moku:Pro
Moku:Pro General Moku:Pro Arbitrary Waveform Generator Moku:Pro Data Logger Moku:Pro Frequency Response Analyzer Moku:Pro Oscilloscope Moku:Pro PID Controller Moku:Pro Spectrum Analyzer Moku:Pro Waveform Generator Moku:Pro Lock-in Amplifier Moku:Pro Laser Lock Box Moku:Pro Digital Filter Box Moku:Pro FIR Filter Builder Moku:Pro Phasemeter Moku:Pro Multi-instrument Mode Moku:Pro Logic Analyzer/Pattern Generator Moku:Pro Time & Frequency Analyzer
- Python API
- MATLAB API
- Arbitrary Waveform Generator
- Data Logger
- Digital Filter Box
- FIR Filter Builder
- Frequency Response Analyzer
- Laser Lock Box
- Lock-in Amplifier
- Oscilloscope
- Phasemeter
- PID Controller
- Spectrum Analyzer
- Time & Frequency Analyzer
- Waveform Generator
- Logic Analyzer & Pattern Generator
- Multi Instrument Mode
- Moku Cloud Compile
- Moku general
- LabVIEW
External:
The External mode directly multiplies the signals from input 1 and input 2, which is particularly useful when the modulation signal is not sinusoidal. For instance, if the modulation signal is a low-duty-cycle pulse, direct multiplication significantly enhances the demodulation spectral coverage compared to sinusoidal demodulations. However, in this mode, the lock-in amplifier can only demodulate the X (in-phase) component and cannot calculate R or theta.
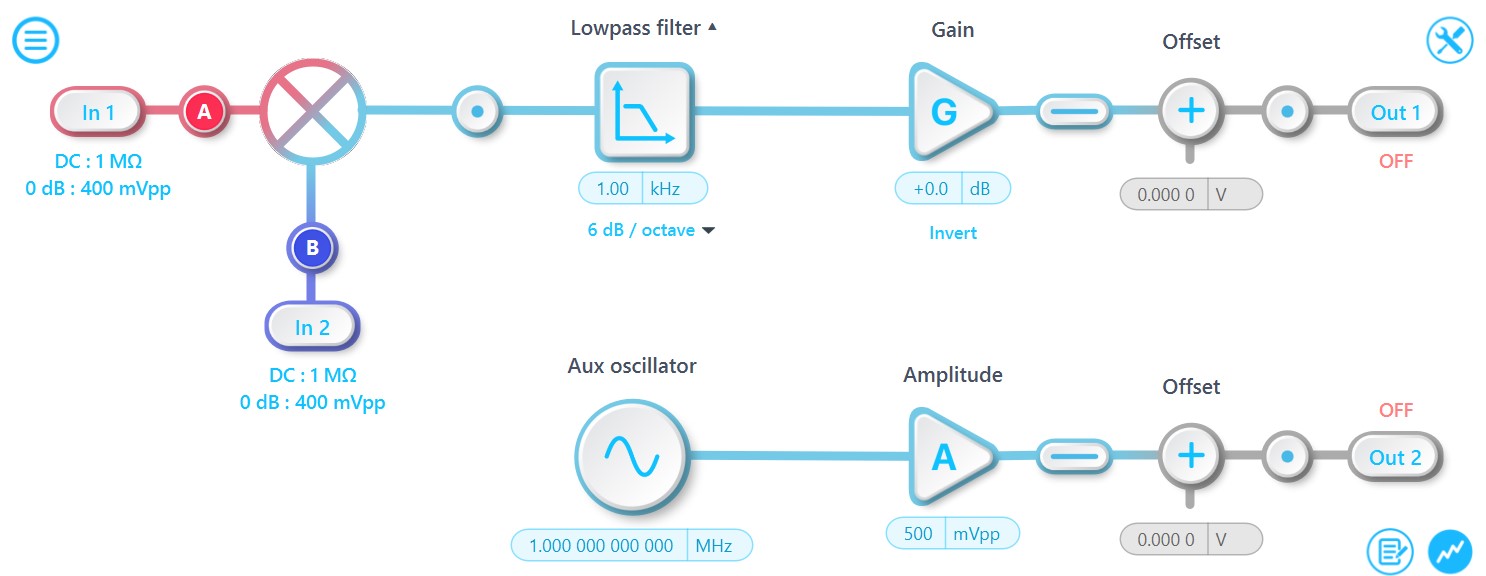
External (PLL):
When the modulation signal is a single-tone signal (sine wave), the External demodulation mode performs worse than the External (PLL) mode because it includes noise from both inputs in the final measured results. The External (PLL) establishes a phase-locked loop with input 2 and generates a pair of noiseless sinusoidal waves at the same frequency for dual-phase demodulation. This allows the user to access the X, Y, R, and theta directly from the lock-in amplifier. The user can also fine-tune the phase of the local oscillator with this mode. This is the recommended external reference mode for most use cases.